什么是runtime? 简单来说,runtime就是一个C语言库,包含了很多底层C语言的API。Objective-C语言是一门动态语言,我们平时变编写的Objective-C代码,在程序运行时,最终都是转成了runtime的C语言代码。所以,只有在程序运行时,才会去确定对象的类型,并调用类与对象相应的方法。
利用runtime能做什么? 利用runtime机制让我们可以在程序运行时动态修改类对象、对象中的所有属性、方法,就算是私有方法以及私有属性都是可以动态修改的。KVO的底层实现就是利用runtime来实现的
类和对象基本数据结构 首先,我们来认识一下classes和objects的概念。我们都知道,Objects是由Classes生成,但是在Objective-C中,Classes本身也是objects,也能处理消息,这也就是为什么有类方法和实例方法。
Class 打开objc.h可以看到Class的定义
1 typedef struct objc_class *Class;
Class 实际上就是一个指向 objc_class 结构体的指针,打开 objc/runtime.h 中查看 objc_class 的定义
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 struct objc_class { Class isa OBJC_ISA_AVAILABILITY; #if !__OBJC2__ Class super_class OBJC2_UNAVAILABLE; const char *name OBJC2_UNAVAILABLE; long version OBJC2_UNAVAILABLE; long info OBJC2_UNAVAILABLE; long instance_size OBJC2_UNAVAILABLE; struct objc_ivar_list *ivars OBJC2_UNAVAILABLE; struct objc_method_list **methodLists OBJC2_UNAVAILABLE; struct objc_cache *cache OBJC2_UNAVAILABLE; struct objc_protocol_list *protocols OBJC2_UNAVAILABLE; #endif } OBJC2_UNAVAILABLE;
但是,上面的代码有 OBJC2_UNAVAILABLE 标志,这是说明这个结构体在 OC 2.0 版本(2006年发布)已经是不可用的,现在已经变成这个样子:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 typedef struct objc_class *Class;typedef struct objc_object *id ;struct objc_object {private: isa_t isa; } struct objc_class : objc_object { Class superclass; cache_t cache; class_data_bits_t bits; }
objc_object 和 objc_class 就是我们经常会用到的 id 和 Class 类型。
objc_object 只包含一个 isa_t 类型的结构体,objc_class 继承于 objc_object,可以得出结论,对象都是有 isa 的,OC中类也是一个对象,那 isa 有什么作用?
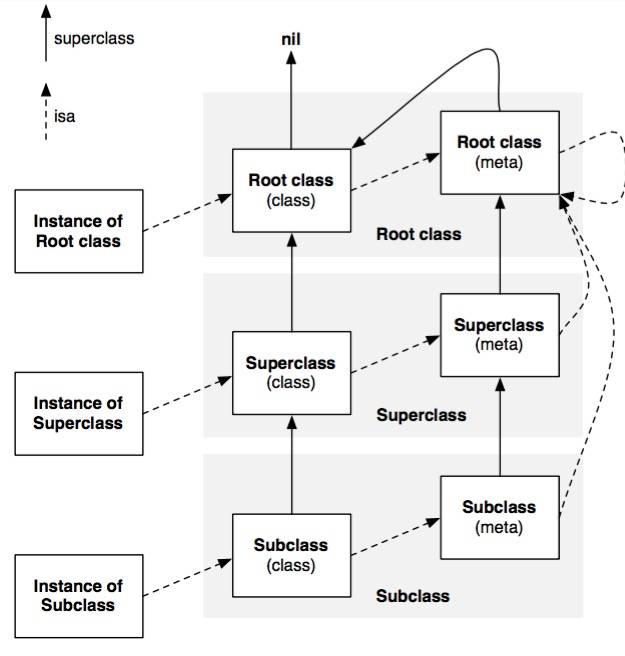
当一个对象的实例方法被调用的时候,就会通过 isa 找到对应的类,然后通过该类的 class_data_bits_t 找到对应的实现。如果调用类方法的话,类对象的 isa 就是元类(meta-class)。对象,类,元类之间的关系:
实线是 super_class 指针,虚线是 isa 指针。
Root class 其实就是 NSObject,它是没有超类的,superclasss 指向 nil。
NSObject 的元类的 superclass 指向自己。
每个元类对象的 isa 都指向 根元类对象。
cache_t 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 typedef unsigned int uint32_t;typedef uint32_t mask_t; typedef unsigned long uintptr_t;typedef uintptr_t cache_key_t;struct cache_t { struct bucket_t *_buckets; mask_t _mask; mask_t _occupied; } struct bucket_t {private: cache_key_t _key; IMP _imp; }
cache_t 里面用散列表来缓存曾经调用过的方法,可以提高方法的查找速度。
class_data_bits_t 使用 bits & FAST_DATA_MASK 可以得到 class_rw_t
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 struct class_rw_t { uint32_t flags; uint32_t version; const class_ro_t *ro; method_array_t methods; property_array_t properties; protocol_array_t protocols; Class firstSubclass; Class nextSiblingClass; char *demangledName; } struct class_ro_t { uint32_t flags; uint32_t instanceStart; uint32_t instanceSize; #ifdef __LP64__ uint32_t reserved; #endif const uint8_t * ivarLayout; const char * name; method_list_t * baseMethodList; protocol_list_t * baseProtocols; const ivar_list_t * ivars; const uint8_t * weakIvarLayout; property_list_t *baseProperties; method_list_t *baseMethods() const { return baseMethodList; } };
class_rw_t 里面的 methos、properties、protocols是可读可写的二维数组,包含了类的初始内容、分类的内容。class_ro_t 里面的 baseMethodList,baseProtocols ,ivars,baseProperties 是只读的一维数组,包含了类的初始内容。
method_t method_t 是对方法的封装。
1 2 3 4 5 struct method_t { SEL name; const char *types; IMP imp; };
runtime 的源码是开源,可以在官方 下载,但是官方的是编译不过的,可以到这里 下载可以编译的版本
objc_msgSend 平常我们使用OC代码来调用方法
1 2 3 4 5 6 People *p = [[People alloc] init]; [p doSomething];
对象调用方法,本质上就是给对象”发送消息”,所以以上的代码,在编译时就会转换成runtime的objc_msgSend函数调用
1 objc_msgSend(p, @selector (doSomething));
objc_msgSend函数会根据接收者和SEL选择器的类型来调用适当的方法,为了完成这个操作,它首先会在自身的isa指针找到自己所属的类(class),然后在这个类(class)的”方法列表”(list of methods)查找该方法,如果找到,就会去执行这个方法。如果找不到,会继续通过自身的super_class指针找到父类的类对象继续查找。如果到最后还是找不到相对应的方法,就会执行”消息转发”操作(将在下文详细介绍)
objc_msgSend函数只能处理部分消息的调用过程,如果有其他“特殊”的情况就会调用另外一些函数来处理,具体会调用哪些函数呢?
1 2 3 objc_msgSend_stret: 发送的消息要返回结构体,就可以用这个函数来发送和接收返回值 objc_msgSend_fpret : 发送的消息要返回浮点数,就可以用这个函数来发送和接收返回值 objc_msgSendSuper : 如果要给超类发送信息,例如[super doSomething]就可以用这个函数来处理。
Runtime实战 终于写到这里了,上文说过runtime可以在程序运行时动态添加类、对象、属性、方法等。那我们可以…生成一个”女朋友”?那下面我们来具体实现一下吧
女朋友养成计划 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 #import "AppDelegate.h" #import <UIKit/UIKit.h> #import <objc/message.h> void cooking(id self ,SEL _cmd,id dish){ Ivar nameIvar = class_getInstanceVariable([self class ], "_name" ); id name = object_getIvar(self , nameIvar); NSInteger age = [[self valueForKeyPath:@"age" ] integerValue]; NSLog (@"动态添加的女朋友名字是%@,年龄:%ld" ,name,age); } int main(int argc, char * argv[]) { @autoreleasepool { Class GirlFriend = objc_allocateClassPair([NSObject class ], "GirlFriend" , 0 ); class_addIvar(GirlFriend, "_name" , sizeof (NSString *), log2(sizeof (NSString *)), @encode (NSString *)); class_addIvar(GirlFriend, "_age" , sizeof (NSInteger ), sizeof (NSInteger ), @encode (NSInteger )); SEL cook = sel_registerName("cooking" ); class_addMethod(GirlFriend, cook, (IMP)cooking, "v@:@" ); objc_registerClassPair(GirlFriend); id gfInstance = [[GirlFriend alloc] init]; Ivar nameIvar = class_getInstanceVariable(GirlFriend, "_name" ); object_setIvar(gfInstance, nameIvar, @"娃娃" ); [gfInstance setValue:@18 forKeyPath:@"age" ]; objc_msgSend(gfInstance,cook,@"鱼香肉丝" ); gfInstance = nil ; objc_disposeClassPair(GirlFriend); return UIApplicationMain (argc, argv, nil , NSStringFromClass ([AppDelegate class ])); } }
以上的函数有几个需要解释一下:
class_addIvar:除了第四个参数,相信其他的参数大家都能知道是什么意思.第四个参数我看了下官方文档的解释
The instance variable’s minimum alignment in bytes is 1<<align. The minimum alignment of an instance variable depends on the ivar’s type and the machine architecture. For variables of any pointer type, pass log2(sizeof(pointer_type)).
成员变量的最小对齐长度是1<<align.这个取决于ivar的类型和机器的架构。任何指针类型的变量,通过log2(sizeof(pointer_type))来进行赋值,而且这个函数只能在objc_allocateClassPair和objc_disposeClassPair之间调用.
class_addMethod:最后一个参数,要赋值的是函数的类型。一个函数至少有两个参数(self和_cmd),这两个参数是隐式参数。函数的类型= 返回值+参数类型,v 表示 void,@ 表示对象,: 表示SEL
objc_disposeClassPair : 如果要销毁的类的实例或者它子类的实例还存在,不能调用这个函数。所以一定要先销毁实例再去销毁类
额外补充 在上面的代码中,我们动态创建了类和成员变量,给类添加方法..但是还没有尝试过添加属性。因为添加属性比较麻烦,所以我打算单独给大家说明一下添加属性这个函数的具体使用.
1 class_addProperty(__unsafe_unretained Class cls, const char *name, const objc_property_attribute_t *attributes, unsigned int attributeCount)
上面的函数用来添加属性,但是第三个参数和第四个参数我们该怎么赋值呢。第三个参数是一个指向objc_property_attribute_t的指针,首先看下它到底是什么
1 2 3 4 5 typedef struct { const char *name; const char *value; } objc_property_attribute_t;
知道了这是一个结构体,看下文档说明
attributes:An array of property attributes.
attributes 就是一个数组,里面装着property的attributes(属性).
知道了attributes是什么了之后,那么问题来了, property 的 attributes是什么呢? 要怎么填?
runtime有一个函数可以拿到property的attributes(属性).那么我们可以试试打印一下看看那是个什么东西.首先,创建一个”MyClass”文件
1 2 3 @interface MyClass : NSObject @property (nonatomic ,copy ) NSString *name;@end
然后随便找个地打印一下
1 2 3 4 5 objc_property_t property = class_getProperty([MyClass class ], "name" ); const char * attribute = property_getAttributes(property);NSLog (@"%s" ,attribute);
输出结果:T@”NSString”,C,N,V_name
The string starts with a T followed by the @encode type and a comma, and finishes with a V followed by the name of the backing instance variable. Between these, the attributes are specified by the following descriptors, separated by commas
就是说这个字符串是以T跟着类型编码和逗号开头,以V成员变量的名称结束
看到这里我们有能明白了,attributes要赋值一个objc_property_attribute_t结构体类型的数组,而objc_property_attribute_t结构体要赋值的是property的属性。so 我们动手尝试一下吧
1 2 3 4 5 6 objc_property_attribute_t type1 = {"T" ,"@\"NSString\"" }; objc_property_attribute_t policy = {"C" ,"" }; objc_property_attribute_t rmw = {"N" ,"" }; objc_property_attribute_t ivar = {"V" ,"_introduction" }; objc_property_attribute_t att[] = {type1,policy,rmw,ivar}; class_addProperty(GirlFriend, "introduction" , att, 4 );
了解女朋友 了解自己的女朋友是必不可少的,那么我们怎么通过代码来了解呢?
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 @interface GirlFriend : NSObject { NSString *_nativeplace; NSString *_background; } @property (nonatomic ,copy ) NSString *name;@property (nonatomic ,assign ) NSUInteger age;@property (nonatomic ,assign ) double height;- (void )AllIvars; - (void )AllPropertys; - (void )cooking; - (void )fitness; - (void )AllMethods; @end
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 #import "GirlFriend.h" #import <objc/message.h> @implementation GirlFriend - (void )AllIvars { unsigned int outCount = 0 ; Ivar *ivars = class_copyIvarList(self .class, &outCount); for (int i = 0 ; i < outCount; i++) { Ivar ivar = ivars[i]; const char * ivarName = ivar_getName(ivar); NSLog (@"ivarName--%s" ,ivarName); } free(ivars); } - (void )AllPropertys { unsigned int outCount = 0 ; objc_property_t *propertys = class_copyPropertyList(self .class, &outCount); for (int i = 0 ; i < outCount; i++) { objc_property_t property = propertys[i]; const char * propertyName = property_getName(property); NSLog (@"propertyName--%s" ,propertyName); } free(propertys); } - (void )AllMethods { unsigned int outCount = 0 ; Method *methods = class_copyMethodList(self .class, &outCount); for (int i = 0 ; i < outCount; i++) { Method method = methods[i]; SEL methodName = method_getName(method); NSLog (@"methodName--%@" ,NSStringFromSelector (methodName)); } free(methods); } @end
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 int main(int argc, char * argv[]) { @autoreleasepool { GirlFriend *gf = [[GirlFriend alloc] init]; [gf AllIvars]; [gf AllPropertys]; [gf AllMethods]; return UIApplicationMain (argc, argv, nil , NSStringFromClass ([AppDelegate class ])); } }
输出结果:
以上的函数都比较简单.但是很实用,比如快速归档和解档.而且要注意一点,因为runtime是C语言的函数,所以遇到copy创建的对象基本上都要用free()函数来释放.
关联对象的使用 我们可以通过关联对象给女朋友添加属性。首先创建一个女朋友的分类Extension
1 2 3 4 5 #import "GirlFriend.h" @interface GirlFriend (Extension )@property (nonatomic ,copy ) NSString *personality;@end
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 #import "GirlFriend+Extension.h" #import <objc/runtime.h> @implementation GirlFriend (Extension )- (void )setPersonality:(NSString *)personality { objc_setAssociatedObject(self , @selector (personality), personality, OBJC_ASSOCIATION_COPY_NONATOMIC); } - (NSString *)personality { return objc_getAssociatedObject(self , @selector (personality)); }
关联对象是比较简单的,用得场景也很多.可以看下第三方库的源码.关联对象很常用,.不仅仅是添加属性.
字典转模型 相信大家都使用过第三方库来实现这个功能,下面我们来了解一下这个功能的具体实现
1 2 3 4 #import <Foundation/Foundation.h> @interface NSObject (KeyValue )+ (instancetype )modelWithDictonary:(NSDictionary *)dict; @end
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 #import "NSObject+KeyValue.h" #import <objc/message.h> @implementation NSObject (KeyValue )+ (instancetype )modelWithDictonary:(NSDictionary *)dict { id instance = [[self alloc] init]; unsigned int outCount = 0 ; Ivar *ivars = class_copyIvarList(self , &outCount); for (int i = 0 ; i < outCount; i++) { Ivar ivar = ivars[i]; NSString *name = [NSString stringWithUTF8String:ivar_getName(ivar)]; NSString *key = [name substringFromIndex:1 ]; id value = dict[key]; if (value) { [instance setValue:value forKey:key]; } } return instance; } @end
简单实现了具体功能,而且也解决了字典中的key找不到对应的属性也不会Crash
method swizzling 之前提到了方法调用其实就是发消息给对象,那么当对象接收到了消息之后怎么调用对应的方法呢?
消息机制原理:对象根据方法编号SEL在”方法映射表”中找到对应的方法实现.因为Objective-C是动态语言,具体要调用哪个方法要到运行时才决定。所以,我们可以在运行时把SEL对应的方法实现改变一下.我们可以在不修改源码和继承子类覆写方法就能修改一个类本身的功能。这种方法叫method swizzling(俗称”黑魔法”)
回到GirlFriend.h文件,我们给女朋友添加“做家务”的功能
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 - (void )housework { NSLog (@"做家务" ); } - (void )cooking { NSLog (@"做饭" ); }
需求:让女朋友做饭,她却去做家务
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 + (void )load { Method cooking = class_getInstanceMethod(self , @selector (cooking)); Method housework = class_getInstanceMethod(self , @selector (housework)); method_exchangeImplementations(housework, cooking); }
然后随便找个地验证一下
1 2 GirlFriend *gf = [[GirlFriend alloc] init]; [gf cooking];
上面的例子只是简单的交换方法。method swizzling也可以交换系统自带的方法.也能在系统原有的功能里,添加更多的功能。或者迭代开发中处理版本兼容问题也能用到
消息转发机制 上文说了消息传递机制的原理,那么我们可能还会遇到另一种情况,当发送消息给对象的时候,对象不能解析这条消息(找不到对应的方法)会方法什么情况呢?
当一个对象收到不能解析的消息之后,就会启动”消息转发”机制。我们可以在这个过程告诉对象应该怎么处理!
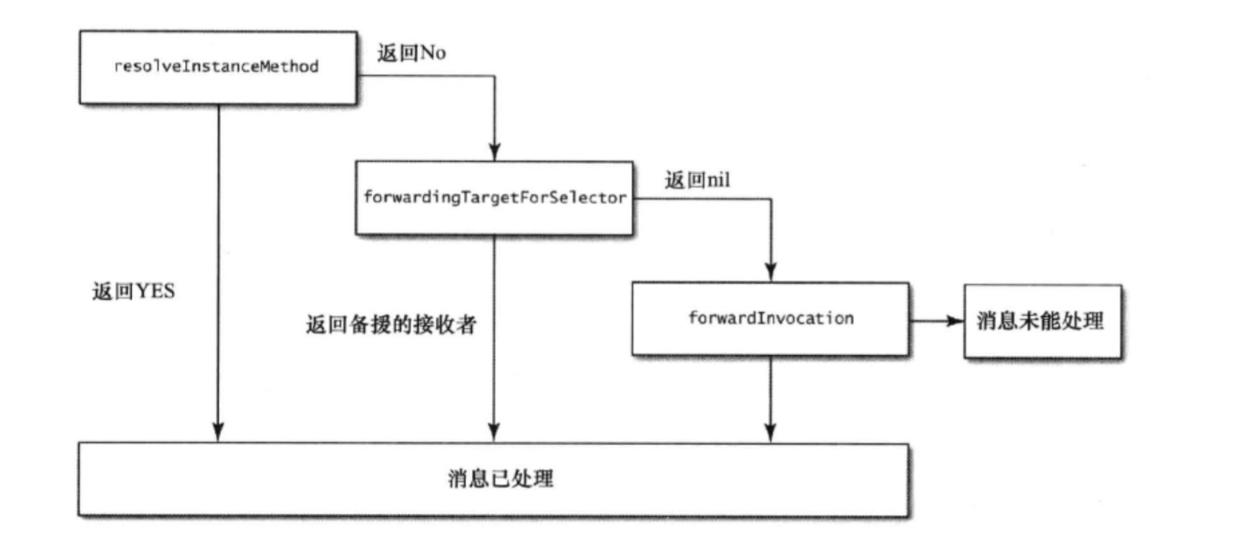
动态方法解析
1 + (BOOL )resolveInstanceMethod:(SEL)sel
其返回值是BOOL类型,表示这个是否能新增一个实例方法来处理此选择子,返回NO的话进入下一步
备援接收者
1 - (id )forwardingTargetForSelector:(SEL)aSelector
如果返回nil的话就进入下一步
完整的消息转发NSInvocation对象来进行处理(下文详解)。这个步骤会调用下面方法来进行转发消息
1 - (void )forwardInvocation:(NSInvocation *)invocation
看张图片加深理解
模拟场景:如果我们找了一个“女朋友”,谈的时候她跟你说她做饭很好吃!!,等你带回家的时候,发现她根本就不会做饭.这不是坑爹吗?那我们应该怎么办呢?cooking方法的实现给注释掉.
1 2 GirlFriend *gf = [[GirlFriend alloc] init]; [gf cooking];
报错:
1 2 -[GirlFriend cooking]: unrecognized selector sent to instance 0x7fbef2e0b490 Terminating app due to uncaught exception 'NSInvalidArgumentException', reason: '-[GirlFriend cooking]: unrecognized selector sent to instance 0x7fbef2e0b490'
报错的原因是:你的女朋友根本就不会做饭..
第一步 让女朋友会做饭 在GrilFriend.m文件
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 + (BOOL )resolveInstanceMethod:(SEL)sel { class_addMethod(self , sel, (IMP)cooking, "v@:" ); return YES ; } static void cooking(id self ,SEL _cmd){ NSLog (@"会做饭啦" ); }
随便找块地打印
1 2 GirlFriend *gf = [[GirlFriend alloc] init]; [gf cooking];
第二步 让别人来做饭 如果你的女朋友死活不肯去做饭呢?那我们请个保姆做呗..
1 2 3 @interface Nurse : NSObject - (void )cooking; @end
.m文件
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 @implementation Nurse - (void )cooking { NSLog (@"保姆去做饭啦" ); }
回到GirlFriend.m文件
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 + (BOOL )resolveInstanceMethod:(SEL)sel { return NO ; } - (id )forwardingTargetForSelector:(SEL)aSelector { Nurse *n = [[Nurse alloc] init]; return n; }
好了,那我们随便找块地打印验证一下
1 2 GirlFriend *gf = [[GirlFriend alloc] init]; [gf cooking];
第三步 完整的消息转发 来到这一步的话,说明就要创建并且处理NSInvocation对象。这个对象用起来比较麻烦。所以一般都会在前两步来处理(最好在第一步)
下面我们来使用一下NSInvocation对象
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 - (NSMethodSignature *)methodSignatureForSelector:(SEL)aSelector { NSMethodSignature *sig = [NSMethodSignature signatureWithObjCTypes:"v@:" ]; return sig; } - (void )forwardInvocation:(NSInvocation *)anInvocation { [anInvocation setTarget:self ]; [anInvocation setSelector:@selector (invocation)]; [anInvocation invoke]; } - (void )invocation { NSLog (@"通过invocation调用" ); }
打印一下
1 2 3 GirlFriend *gf = [[GirlFriend alloc] init]; [gf cooking];
额外补充
1 2 3 4 anInvocation setArgument:(nonnull void *) atIndex:(NSInteger )
参考文献 运行时之一:类与对象 Effective Objective C 2.0:编写高质量iOS与OS X代码的52个有效方法 让你快速上手Runtime